NVIDIA tensor cores
Overview and evaluation of tensor cores
Tensor cores are firstly embedded in Volta architecture (CUDA 9), in Turing they are using the second generation, in Ampere the 3rd generation and 4th generation in Hopper
Tensor Cores in Volta V100
Key take aways
In Volta GV100, each Tensor Core performs 64 floating point FMA operations per clock, and eight Tensor Cores in an SM perform a total of 512 FMA operations (or 1024 individual floating point operations) per clock.
Tensor Cores provide up to 12x higher peak TFLOPS on Tesla V100 that can be applied to deep learning training compared to using standard FP32 operations on P100
Each Tensor Core operates on a 4x4x4 matrix and performs the following operation: D = A×B + C, where A/B can be FP16 and C/D can be FP16/FP32
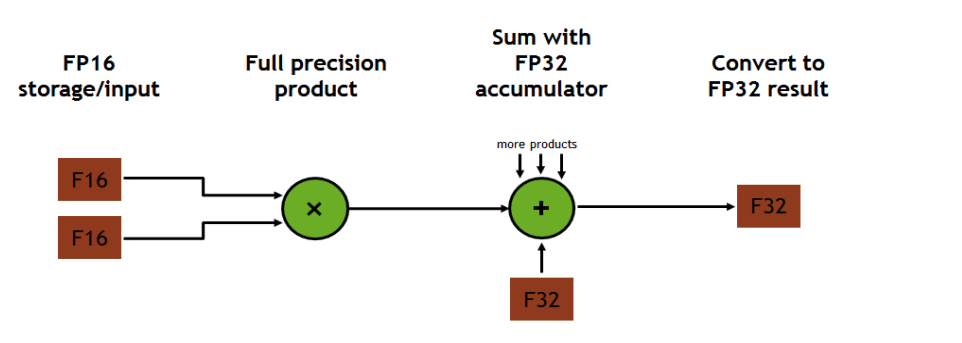
Inputs are FP16; Full precision produce; FP32 accumulation.
Manipulate methods
- CUDA C++ API. The API exposes specialized matrix load, matrix multiply and accumulate, and matrix store operations to efficiently use Tensor Cores from a CUDA-C++ program.
- cuBLAS and cuDNN libraries.
Tensor Cores in Turing
Key take aways
- Add new INT8 and INT4 for inferencing.
- A new technique called Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) is powered by Tensor Cores
Tensor Cores in Ampere
GA10X Key take aways
- Introduce hardware support for processing matrices with specific sparsity patterns at up to 2x throughput, by skipping the zero-valued elements.
- Add new precision mode TF32 and BF16.
- Note that GA10x GPUs do not include Tensor Core acceleration for double-precision (FP64) operations, as provided in A100.
A100 Key take aways
For HPC, the A100 Tensor Core includes new IEEE-compliant FP64 processing that delivers 2.5x the FP64 performance of V100.
- TF32 Tensor Core instructions which accelerate processing of FP32 data
- IEEE-compliant FP64 Tensor Core instructions for HPC
- BF16 Tensor Core instructions at the same throughput as FP16
Each of the A100 Tensor Cores can execute 256 FP16 FMA operations per clock, allowing it to compute the results for an 8x4x8 mixed-precision matrix multiplication per clock
A100 accelerates tensor math with TF32 while supporting FP32 input and output data (right), enabling easy integration into DL and HPC programs and automatic acceleration of DL frameworks.
FP64 facility
- For HPC community.
- Delivering up to 2.5x the FP64 performance of the NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPU
- The new Double Precision Matrix Multiply Add instruction on A100 replaces 8 DFMA instructions on V100, reducing instruction fetches, scheduling overhead, register reads, datapath power, and shared memory read bandwidth.
- The Tensor Core Accelerated Iterative Refinement Solver (TCAIRS) in cuSOLVER automates usage of mixed precision for this application.
- Last year, a fusion reaction study for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor demonstrated that mixed-precision techniques delivered a speedup of 3.5x on V100 for such solvers using V100’s FP16 Tensor Cores. The same technology used in that study tripled the Summit supercomputer’s performance on the HPL-AI benchmark.
Comparison of these three generations
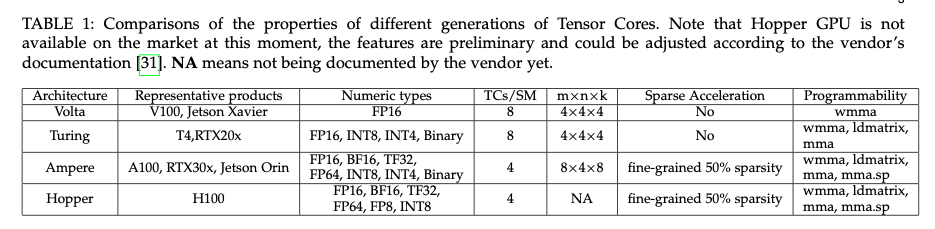
- From [[Dissecting the NVidia Turing T4 GPU via Microbenchmarking.pdf]]
Ways to manipulate tensor cores
- High-level libraries like cuBLAS and cuDNN
- CUDA C++ API (WMMA)
- PTX
- Device
Example of 1, 2 in Programming Tensor Cores in CUDA 9
Example of 3, 4 in [[NVIDIA cutlass, PTX to program tensor cores.pdf]]